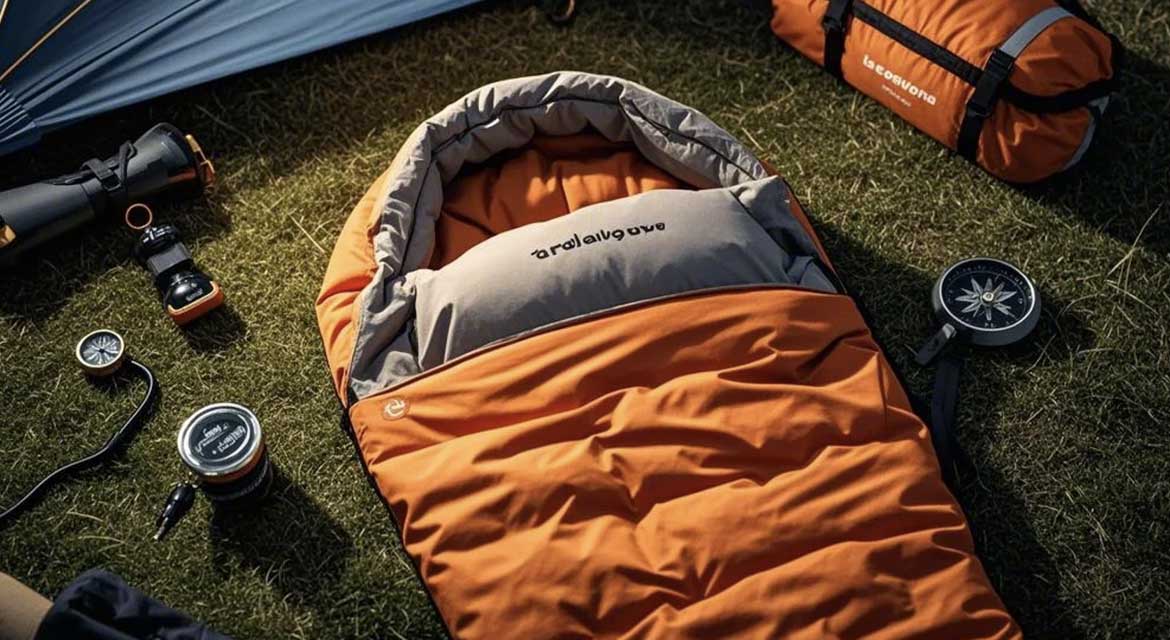
Sleeping Bags
Type
Mummy, Rectangular, Quilt

Material
Lightweight Nylon Or Polyester (20d–40d), With Water-Resistant Coatings

Insulation
Down, Synthetic

ECO
Recycled shell fabrics, PFC-free DWR, or plant-based synthetics.
- 1. Design and Prototyping
- Concept Development: Define the sleeping bag type (e.g., mummy, rectangular, quilt), temperature rating (seasonal use), and target audience (campers, mountaineers, children).
- Technical Specifications:
- CAD modeling for shape, size, and insulation distribution.
- Features like hoods, draft collars, zipper baffles, and pad attachment systems.
- Prototyping: Test prototypes in climate chambers to validate thermal efficiency and comfort.
2. Material Selection- Shell and Lining Fabrics:
- Lightweight nylon or polyester (20D–40D), often with water-resistant coatings (DWR).
- Ripstop weaves for durability.
- Insulation:
- Down: High-fill-power goose/duck down (e.g., 600–900 fill power), ethically sourced (RDS-certified).
- Synthetic: Hollow-core fibers (e.g., PrimaLoft®, Thermolite) for moisture resistance.
- Zippers: YKK® anti-snag zippers with draft tubes.
- Sustainability: Recycled shell fabrics, PFC-free DWR, or plant-based synthetics.
3. Fabric Cutting- Pattern Making: Convert 3D designs into 2D panels (shell, lining, hood).
- Laser/Ultrasonic Cutting: Precision-cut fabrics to minimize waste.
- Baffle Layout: Mark baffle (compartment) lines to contain insulation and prevent cold spots.
4. Insulation Application- Down Filling:
- Down is cleaned, sterilized, and blown into baffles using specialized machines.
- Baffles are sewn/glued to prevent shifting (box baffle, slant baffle, or sewn-through stitching).
- Synthetic Filling:
- Layered sheets or loose fibers are stitched between shell and lining.
- Continuous filament construction for better loft retention.
5. Sewing and Assembly- Shell and Lining Stitching: Sew outer shell and inner lining panels, leaving openings for zippers and insulation.
- Baffle Construction: Attach vertical/horizontal baffles to create insulated compartments.
- Zipper Integration: Sew zippers with draft tubes to block heat loss.
- Hood and Draft Collar: Add adjustable hoods and insulated collars around the neck.
- Reinforcements: Bar tacks at stress points (zipper ends, shoulder areas).
6. Quality Control- Thermal Testing:
- EN 13537/ISO 23537 certification for temperature ratings (comfort, limit, extreme).
- Climate chamber tests to simulate cold conditions.
- Durability Checks:
- Zipper cycle tests (500+ openings/closings).
- Seam strength and insulation distribution checks.
- Safety Compliance: Ensure non-toxic materials and flame resistance (CPAI-75).
7. Finishing and Packaging- Compression: Roll or stuff into a compression sack with a stuff sack included.
- Labeling: Add temperature ratings, care instructions, and eco-certifications (e.g., Bluesign®).
- Retail Packaging: Folded in branded bags or boxes for shelf appeal.





