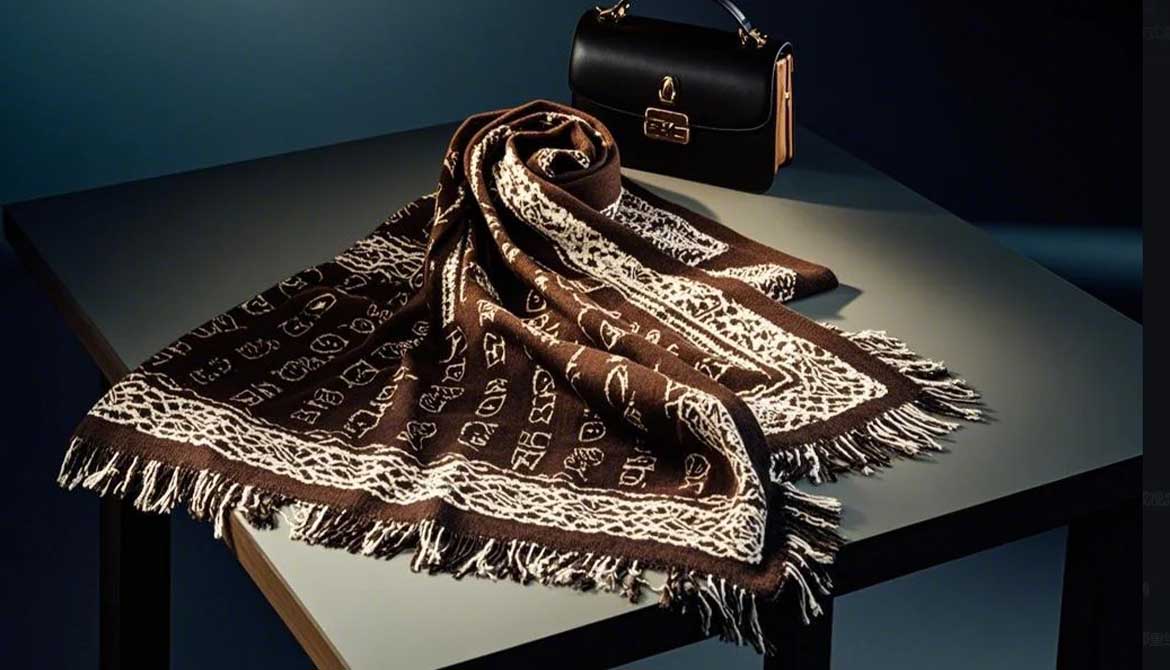
Shawls
Yarns
Wool, Silk, Cotton, Polyester Or Acrylic

Embroidery
High Density Embroidery Machine

Printing
Screen Printing, Thermal Transfer, Digital Direct Printing, Etc.

ECO
Organic Cotton, Recycled Polyester, Etc
- 1. Material Selection
- Natural Fibers:
- Wool: Sheared from sheep, goats (e.g., cashmere, pashmina), or alpacas.
- Silk: Harvested from silkworm cocoons; known for its luster and softness.
- Cotton: Ginned and cleaned to remove seeds and impurities.
- Synthetic Fibers: Polyester or acrylic for affordability and durability.
- Blends: Combinations like wool-silk for enhanced texture and warmth.
- Cleaning:
- Wool: Scoured to remove lanolin and debris.
- Silk: Degummed to extract raw filaments (sericin removal).
- Cotton: Carded to align fibers.
- Spinning:
- Fibers spun into yarn using machines (industrial) or hand-spindles (artisanal).
- Yarn thickness and twist vary based on desired fabric weight.
- Weaving:
- Looms: Warp and weft yarns interlaced (e.g., plain, twill, or jacquard weaves).
- Handlooms: Traditional method for intricate patterns (e.g., Kashmiri Pashmina).
- Knitting:
- Machines or hand-knitting for stretchable, lightweight shawls (e.g., lace designs).
- Dyeing:
- Yarn-Dyed: Colored before weaving for long-lasting vibrancy.
- Piece-Dyed: Fabric dyed post-weaving; common for solid colors.
- Natural vs. Synthetic Dyes: Eco-friendly plant-based dyes or chemical alternatives.
- Printing:
- Block Printing: Hand-carved blocks for traditional motifs.
- Digital Printing: High-precision designs for complex patterns.
- Embroidery: Hand or machine-stitched (e.g., Kashmiri sozni, floral motifs).
- Beading/Sequins: Added for decorative appeal.
- Fringes: Attached to edges via twisting or knotting.
- Washing: Removes excess dye and softens fibers.
- Treatments:
- Mercerization (cotton): Enhances strength and sheen.
- Anti-Shrink (wool): Prevents felting.
- Pressing/Steaming: Ensures smooth texture and shape retention.
- Defect Inspection: Checks for uneven dye, loose threads, or weaving errors.
- Durability Tests: Assess colorfastness, shrinkage, and seam strength.
- Certifications: Compliance with standards (e.g., OEKO-TEX®, GOTS for organic materials).
- Folding/Wrapping: Neatly folded, often with tissue paper to preserve quality.
- Labeling: Tags include material details, care instructions, and origin.
- Sustainable Packaging: Recyclable or biodegradable materials for eco-conscious brands.
- Natural Fibers:





