Squeeze
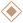
Material
TPE , Silicone

Moldling
3D model, Steel Or Aluminum

Painting
Painting, Coating, Or Texturing

ECO
ASTM, EN71
1. Design and Prototyping
Concept Development: The process begins with brainstorming and conceptualizing the toy’s design, including its shape, size, and functionality.
3D Modeling: Designers create a digital 3D model using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
Prototyping: A physical prototype is created using 3D printing or other methods to test the design, functionality, and ergonomics.
2. Material Selection
Material Choice: The primary material used is usually soft, flexible, and non-toxic, such as TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) or silicone.
Color and Additives: Pigments and other additives are selected to achieve the desired color, texture, and properties (e.g., UV resistance, durability).
3. Mold Making
Mold Design: Based on the finalized 3D model, a mold is designed. The mold is typically made from steel or aluminum for durability.
Mold Fabrication: The mold is precision-machined to ensure accurate replication of the toy’s design.
4. Injection Molding
Material Preparation: The chosen material is prepared, often in pellet form, and fed into an injection molding machine.
Molding Process: The material is heated until molten and then injected into the mold under high pressure. It cools and solidifies into the shape of the toy.
Demolding: Once cooled, the toy is ejected from the mold.
5. Post-Processing
Trimming and Cleaning: Excess material (flash) is trimmed off, and the toy is cleaned to remove any residues.
Surface Treatment: Additional treatments, such as painting, coating, or texturing, may be applied to enhance the toy’s appearance and feel.
6. Quality Control
Inspection: Each toy is inspected for defects, such as air bubbles, uneven surfaces, or color inconsistencies.
Testing: Functional tests may be conducted to ensure the toy meets safety and performance standards (e.g., squeeze resistance, durability).
7. Assembly (if applicable)
Component Integration: If the toy has multiple parts (e.g., squeakers, internal mechanisms), these are assembled at this stage.
Final Assembly: All components are securely attached, and the toy is checked for proper functionality.
8. Packaging
Labeling: The toy is labeled with necessary information, such as branding, safety warnings, and barcodes.
Packaging: The toy is packaged in protective materials (e.g., blister packs, boxes) to prevent damage during shipping and to enhance shelf appeal.
9. Distribution
Storage: Finished products are stored in a warehouse until they are ready for distribution.
Shipping: The toys are shipped to retailers or directly to customers.
10. Post-Market Monitoring
Feedback Collection: Customer feedback is collected to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement: Based on feedback, the design or production process may be refined to enhance product quality and customer satisfaction.
Key Considerations:
Safety: Ensuring the toy is safe for its intended age group, free from harmful chemicals, and complies with relevant regulations (e.g., ASTM, EN71).
Durability: The toy should withstand repeated squeezing and other forms of play without breaking or degrading.
Cost Efficiency: Balancing quality with cost-effective production methods to maintain profitability.





